1. Definition of Threads
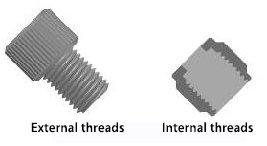
Threads are continuous protrusions in the form of spirals wrapped around a cylindrical or conical body. The former is called straight threads, while the latter is called conical threads. Threads on the outer surface of a workpiece are referred to as external threads, such as those commonly seen on bolts or screws. Threads on the inner surface of a workpiece are called internal threads, like those found in nuts.
2. Five Elements of Threads
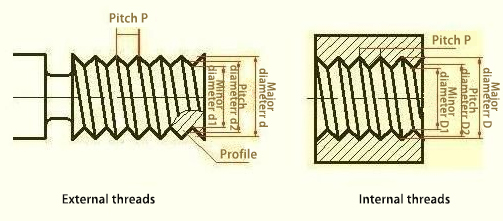
Threads consist of five elements: profile, nominal diameter, number of starts, pitch (or lead), and direction of thread. Among these, the profile is the key element that determines the final application of the thread.
2.1 Profile
The contour shape of the thread in a section through the thread axis is called the profile. Common profiles include triangular, trapezoidal, saw-toothed, and rectangular shapes.
2.2 Nominal Diameter
Threads have major diameter (d, D), pitch diameter (d2, D2), and minor diameter (d1, D1). The nominal diameter, which represents the size of the thread, is used to denote threads. For common threads, the nominal diameter is the major diameter.
2.3 Number of Starts
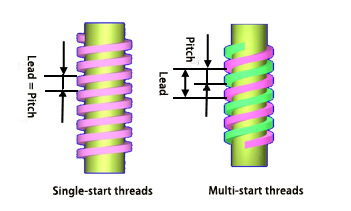
A thread formed along a single helix is called a single-start thread, while a thread formed along two or more helices evenly distributed along the axis is called a multi-start thread.
2.4 Pitch and Lead
The pitch (p) is the axial distance between corresponding points on adjacent threads measured along the pitch diameter.
The lead (ph) is the axial distance between corresponding points on adjacent threads along the same helix measured along the pitch diameter.
For single-start threads, lead = pitch; for multi-start threads, lead = pitch × number of starts.
2.5 Direction of Thread
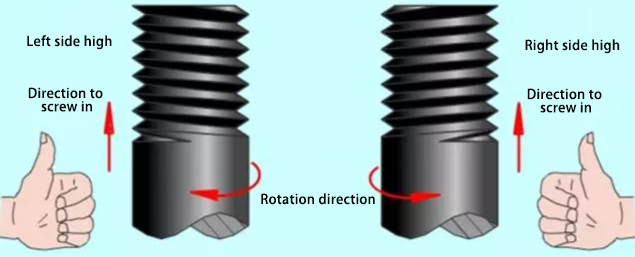
Threads that engage when rotated clockwise are called right-hand threads, while those that engage when rotated counterclockwise are called left-hand threads.
3. Thread Designation and Applications
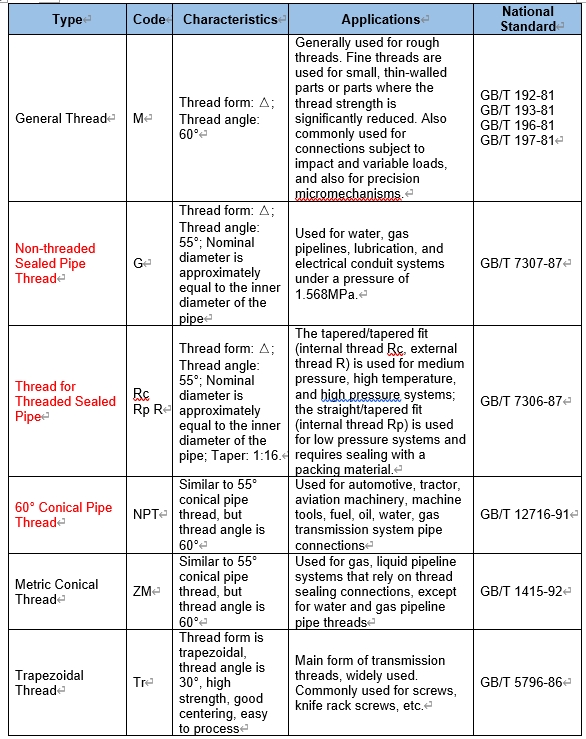
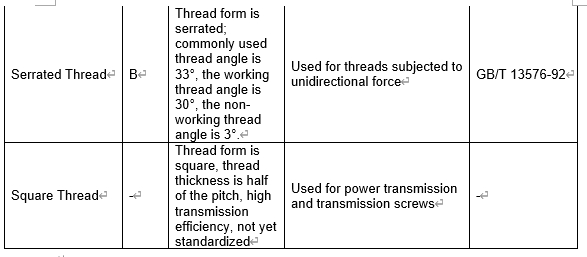
4. Thread and Tap Applicable Precision Grades
4.1 Thread Precision Annotation
Thread precision is a comprehensive indicator of thread quality, composed of thread tolerance zones and engagement length. Thread tolerance zone designations include pitch diameter tolerance zone and crest diameter tolerance zone designations. Tolerance zone designations consist of a tolerance grade number and a letter indicating its position, such as 6g, 6H, etc.
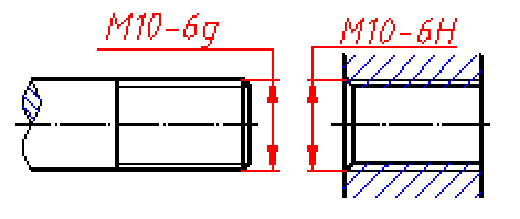
4.2 Correspondence between Taps and Threads
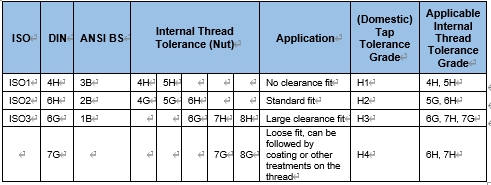
Author: Guo Wei, Qianhao Quality Department